Acme screws are an essential component of many industrial and mechanical processes. These screws are often used to convert rotary motion into linear motion or vice versa, which makes them versatile and essential for many applications. Read More…
Del-Tron Precision, Inc. produces and supplies various automated equipment, such as ball screw actuators. Our engineers have designed our ball screws to offer accuracy that is unparalelled by competitors.
When it comes to ball screws, no one does them better! We offer same day shipping to ensure that your product will be sent to you as soon as possible in order to keep your business moving smoothly.

Wedin International specializes in ball screws of various types and assemblies. We also offer 24-hour product repair. Wedin International provides several industries and applications with high-quality products and services. Wedin covers all types of motion control parts for any application. Call today, we would be glad to discuss your needs and welcome the opportunity in working with you.

More Acme Screw Manufacturers
Variations of Acme Screws: Types, Sizes, and Material Choices
Acme screws, known for their trapezoidal thread profile, are essential components in mechanical power transmission and linear motion systems. There are numerous variations of acme screws, each designed to address specific engineering, load, and operational requirements. Understanding the different types, sizes, and material options is crucial for engineers, procurement specialists, and maintenance professionals seeking optimal performance and reliability from their linear actuators, lead screws, and motion control assemblies.
Acme screw size is a primary factor influencing load capacity, speed, and installation space. Common sizes range from miniature acme screws used in compact medical devices to large-diameter acme screws engineered for heavy industrial equipment, presses, and lifting systems. The pitch and lead of the screw also impact its efficiency, speed of travel, and positional accuracy, making the choice of acme thread form a critical design decision.
Material selection for acme screws is another key consideration. Popular materials include hardened carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and bronze. Each material offers unique advantages for different environments and applications:
- Steel acme screws: Provide high strength and wear resistance, ideal for demanding industrial settings and heavy-duty machinery.
- Stainless steel acme screws: Offer corrosion resistance for food processing, laboratory, or outdoor applications where hygiene or weather exposure is a concern.
- Aluminum acme screws: Lightweight and suitable for weight-sensitive assemblies such as robotics, aerospace, or portable devices.
- Bronze acme screws: Deliver excellent corrosion resistance and low friction, making them a preferred choice for marine environments, chemical processing, and applications prone to galling or seizing.
Design variations, such as single-start, double-start, and multi-start acme screws, further expand the range of available solutions. Multi-start designs enable higher travel speeds and smoother motion, while single-start screws offer greater holding capability and positional stability.
Specific Applications for Each Acme Screw Variation
Acme Screw Size and Its Impact on Application
Choosing the correct acme screw size directly affects an application's load requirements, motion control precision, and mechanical efficiency. Large-diameter acme screws are a staple in machine tools, industrial presses, injection molding machines, and automated assembly lines, where robust motion and force transmission are critical. Smaller acme screws find their place in laboratory automation, pharmaceutical dispensing systems, and medical diagnostics, where fine adjustment and minimal backlash are essential.
Acme Screw Material Selection: Matching Performance to Environment
Material choice is often dictated by operating environment and application-specific demands. For instance, steel acme screws are widely used in construction equipment, mining machinery, and factory automation systems due to their durability. Stainless steel acme screws are preferred in food-grade conveyors, packaging lines, marine steering mechanisms, and any context requiring corrosion resistance or easy cleaning. If reducing system weight is a priority, such as in drone actuation or lightweight robotic arms, aluminum acme screws are ideal. Bronze acme screws are the go-to for applications involving saltwater or aggressive chemicals, such as desalination plants and offshore platforms.
Acme Screw Thread Design: Single-Start vs Double-Start vs Multi-Start
The thread design of an acme screw directly influences speed, load, and precision. Single-start acme screws, featuring a single helical thread, provide reliable self-locking capability and are commonly used in vises, clamps, and manual jacks where holding force is essential. Double-start acme screws, with two threads running parallel, strike a balance between speed and load, making them suitable for semi-automatic presses or moderate-speed actuators. Multi-start acme screws, which may have three or more threads, enable rapid linear motion and are found in CNC machinery, rapid traverse tables, and automation systems where throughput is a priority.
Key Considerations When Specifying Acme Screws
Acme screws offer distinct advantages, but careful consideration must be given to certain limitations and engineering trade-offs:
- Manufacturing Complexity: Acme threads require precise machining or rolling, sometimes leading to higher initial cost compared to standard fasteners or ball screws if custom geometries are needed.
- Efficiency and Friction: Due to their thread angle and surface contact, acme screws produce more friction than ball screws, making them less suitable for ultra-high-speed or continuous-duty motion systems.
- Axial Play and Backlash: Some acme screw assemblies may experience axial play under load, potentially affecting repeatability and accuracy. Preloaded nuts or anti-backlash designs can help mitigate this issue.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: While many acme screws exhibit self-lubricating properties (especially when paired with bronze or engineered polymer nuts), periodic lubrication and inspection are vital for longevity, particularly in high-load or dirty environments.
Benefits of Acme Screws Over Competing Linear Motion Solutions
Examining the unique benefits of acme screws will help you determine if they are the optimal solution for your next linear motion or actuation project. Below are the key advantages that drive engineers and designers to select acme screw assemblies:
High Mechanical Efficiency
Thanks to their robust thread geometry, acme screws provide a large surface area of contact between the acme nut and screw shaft. This design minimizes localized wear, distributes loads evenly, and delivers smooth, reliable motion, even under heavy or shock loads. Compared to square threads or standard lead screws, acme threads operate with less friction than expected due to their optimized flank angle, resulting in reduced energy consumption and minimal heat generation.
Superior Positional Accuracy
Acme screws are synonymous with precision. Their thread profile supports tight manufacturing tolerances, enabling them to achieve and maintain accurate positioning over extended periods. This makes acme screws an excellent choice for CNC machines, coordinate measuring machines, and other applications where repeatability and low backlash are mandatory.
Exceptional Load-Carrying Capability
The trapezoidal thread design of acme screws allows them to transmit high levels of axial force without deformation or premature wear. This trait is particularly valuable in high-load lifting jacks, presses, vises, and industrial automation systems that require reliable, heavy-duty motion control solutions.
Self-Locking Functionality
One of the most prominent advantages of acme screws is their inherent self-locking property. The thread geometry prevents back-driving under load, making acme screws ideal for lifting applications, vertical actuators, and safety-critical systems where accidental descent or movement must be avoided. This eliminates the need for costly external locking mechanisms or brakes in many designs.
Simplified Manufacturing and Adaptability
While high-precision acme screws may require advanced machining, standard acme threads are easier to produce than ball screws or custom thread profiles. They can be manufactured using conventional turning, thread rolling, or even extrusion, making them a cost-effective solution for a wide range of applications, including prototypes and high-volume production runs.
Durability and Reduced Wear
Acme screws are engineered for longevity. Their thread geometry and compatible nut materials (such as bronze, PTFE, or acetal) resist galling, abrasion, and deformation. This durability ensures consistent performance, minimizes downtime, and extends the service life of machinery and automation systems.
Extensive Customization and Configurability
Acme screws are available in a vast array of sizes, lengths, thread pitches, and materials. Custom end-machining, coatings, and pre-assembled nut options enable engineers to tailor acme screw assemblies to their precise performance and installation needs. Whether you need a corrosion-resistant assembly for offshore use or a miniature lead screw for micro-positioning, acme screws offer unmatched flexibility.
Low Noise and Smooth Operation
Compared to recirculating ball screws and some other linear drive systems, acme screws operate with minimal noise and vibration. This makes them ideal for medical devices, laboratory automation, and environments where quiet operation is essential for user comfort or regulatory compliance. If you are seeking linear motion solutions with low acoustic signature, acme screws should be high on your list.
Minimal Maintenance Requirements
Many acme screw assemblies require little ongoing maintenance, especially when paired with self-lubricating nuts or operated in clean environments. When properly specified, they offer reliable, trouble-free service over years of operation. Maintenance can be further reduced with the addition of protective seals or wipers to exclude dust and contaminants.
Cost-Effectiveness and Value
Acme screws offer an attractive balance of performance and affordability, particularly when compared to more complex linear motion solutions. Their straightforward design, robust performance, and ease of integration help lower both initial investment and lifetime operating costs.
Acme Screw Applications: From Industrial Machinery to Precision Devices
Wondering where acme screws are used in real-world applications? Here are some of the most common and high-value use cases across various industries:
- Industrial Automation: Material handling systems, conveyor belt tensioners, machine tools, injection molding machines, and stamping presses.
- Medical Devices: Hospital beds, imaging equipment, prosthetic limb actuation, surgical robots, and laboratory automation platforms.
- Aerospace: Aircraft flap actuation, control surfaces, satellite positioning systems, and spacecraft docking mechanisms.
- Automotive: Electric vehicle seat adjustment, convertible roof actuation, and testing fixtures.
- Robotics: Linear actuators for pick-and-place robots, 3D printer Z-axis controls, and collaborative robot arms.
- Construction: Scissor lifts, hoists, scaffolding actuators, and bridge jacks.
- Marine and Offshore: Ship steering linkages, deck winches, adjustable ramps, and underwater research platforms.
- Consumer Products: Adjustable furniture, home automation lifts, and high-end camera sliders.
- Research & Development: Test stands, scientific instrumentation, and laboratory sample positioning systems.
Looking for a specific acme screw for your application? Consider these questions as you compare acme screw suppliers:
- What are the load, speed, and positional accuracy requirements for my project?
- Which acme screw material and finish will best withstand my operating environment?
- Do I require a standard or anti-backlash acme nut for optimal performance?
- Is noise reduction or smoothness of operation a priority in my application?
- Does my project call for custom end-machining, coatings, or integrated mounting features?
Comparing Acme Screws vs. Ball Screws: Which Linear Actuator Is Best for Your Needs?
Acme screws and ball screws are two of the most popular linear motion technologies, each with its own strengths and ideal use cases. If you are comparing acme screws and ball screws for your next project, consider the following factors:
- Efficiency: Ball screws offer higher mechanical efficiency (up to 90%) due to rolling contact, making them optimal for high-speed, continuous-duty, or energy-sensitive applications. Acme screws, while less efficient, provide superior self-locking and are often more robust for static load situations.
- Load Capacity: Both can handle high loads, but acme screws are better for applications where holding force without back-driving is required. Ball screws are preferred for rapid, repetitive cycling with lower frictional losses.
- Cost: Acme screws are generally more affordable and easier to maintain, while ball screws may cost more due to their complex manufacturing and need for recirculating ball bearings.
- Maintenance: Acme screws have fewer moving parts and are more tolerant of dirt or contamination, whereas ball screws require clean environments and regular lubrication.
Still unsure? Ask yourself: Do I need the high efficiency and speed of a ball screw, or the holding power and simplicity of an acme screw? What is my budget and tolerance for long-term maintenance?
How to Choose the Best Acme Screw Supplier: Key Questions and Evaluation Tips
Selecting the right acme screw manufacturer or distributor is essential for ensuring quality, reliability, and technical support. Here are some proven strategies and questions to guide your search:
- Does the supplier offer a comprehensive range of standard and custom acme screw sizes, thread pitches, and nut options?
- What is the supplier’s experience in your target industry—industrial, medical, aerospace, or otherwise?
- Can they provide documentation, CAD models, and engineering support for integration into your system?
- Do they maintain robust quality control processes, certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), and traceability for material selection?
- Are short lead times, competitive pricing, and after-sales support priorities in your project?
- Can the supplier assist with troubleshooting, installation, and maintenance guidance?
To ensure you have the most positive outcome when purchasing acme screws from an acme screw supplier, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of acme screw suppliers. Each acme screw supplier has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the supplier for more information or to request a quote. Review each acme screw business website using our patented website previewer to quickly learn what each company specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple acme screw companies with the same form.
Frequently Asked Questions About Acme Screws
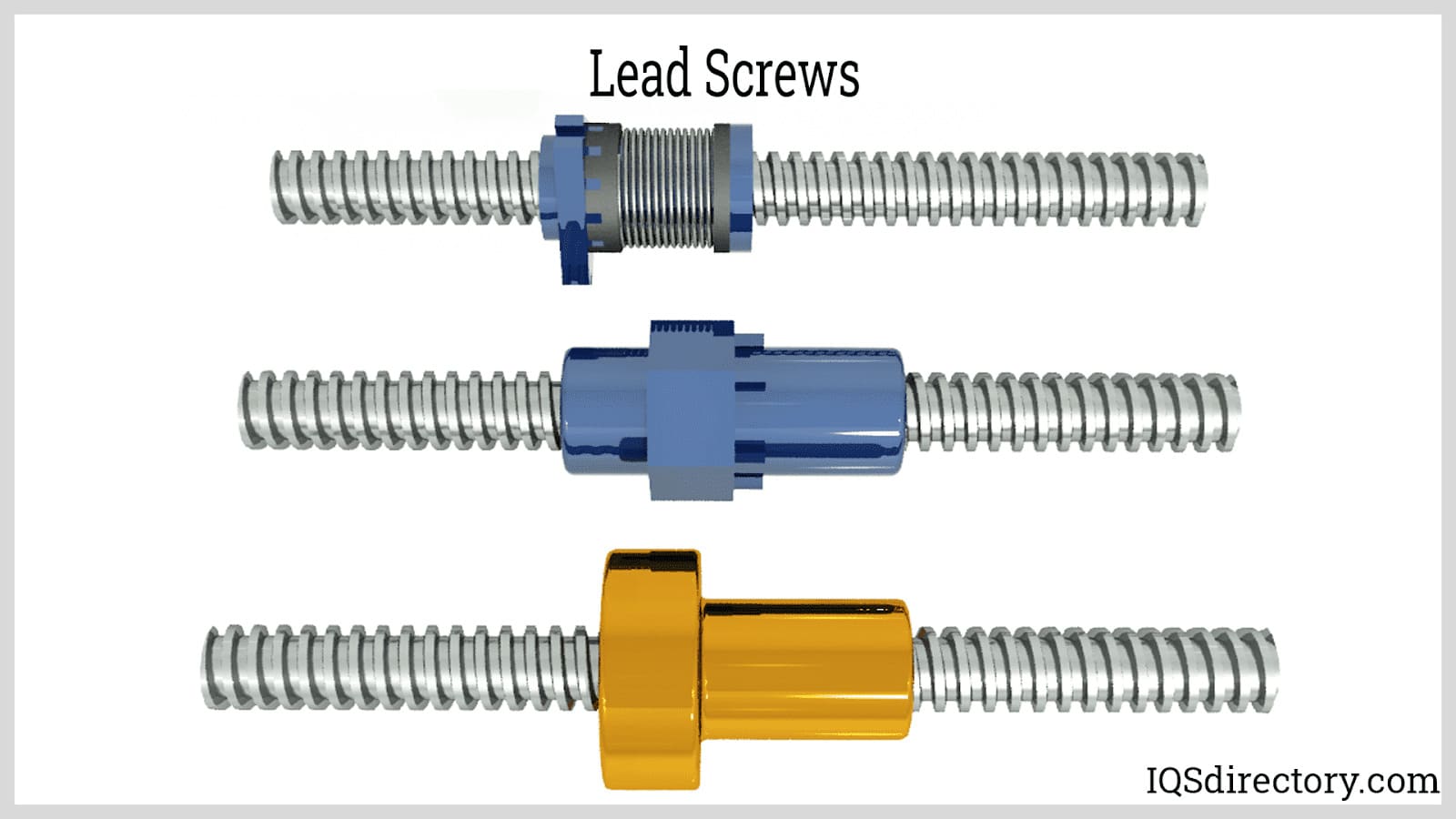
What is the difference between acme screws and lead screws?
While all acme screws are a type of lead screw, not all lead screws use the acme (trapezoidal) thread form. Acme screws are designed for greater load capacity, durability, and self-locking performance, whereas traditional lead screws may use square or buttress threads for specific applications.
When should I use an anti-backlash acme nut?
Anti-backlash acme nuts are ideal for applications demanding high positional accuracy and minimal play, such as CNC machines, 3D printers, and precision laboratory equipment. They compensate for wear and eliminate lash between the screw and nut, ensuring consistent motion and repeatability.
Are acme screws suitable for vertical lifting?
Yes, acme screws are commonly used in vertical lifting applications, including jacks, lifts, and hoists. Their self-locking nature prevents back-driving, making them safer and more reliable for load-holding scenarios.
How do I maintain acme screw assemblies?
Regular cleaning and lubrication are key to extending the life of acme screw assemblies. Choose lubricants compatible with the screw and nut materials, and inspect for signs of wear, contamination, or misalignment. For harsh environments, consider sealed or protected designs.
What industries rely most on acme screws?
Industries such as industrial automation, medical technology, aerospace, automotive manufacturing, robotics, construction, and marine engineering all depend on acme screws for reliable linear motion, load lifting, and precise positioning.
Ready to Source Acme Screws? Start Your Search or Request a Quote
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of acme screw variations, applications, benefits, and selection criteria, you can make a confident, informed decision for your next project. To find the ideal acme screw supplier or manufacturer, explore our acme screw supplier directory and leverage our RFQ tools for fast, accurate quotes tailored to your requirements.
Still have questions about acme screw design, sizing, installation, or troubleshooting? Contact our engineering support team or browse our resource library for:
- Acme screw design guides and technical datasheets
- Installation and maintenance best practices
- Application case studies and real-world success stories
- Custom acme screw and nut options for unique projects
Act now to optimize your linear motion systems with the power and precision of acme screws—trusted across industries for strength, reliability, and value.

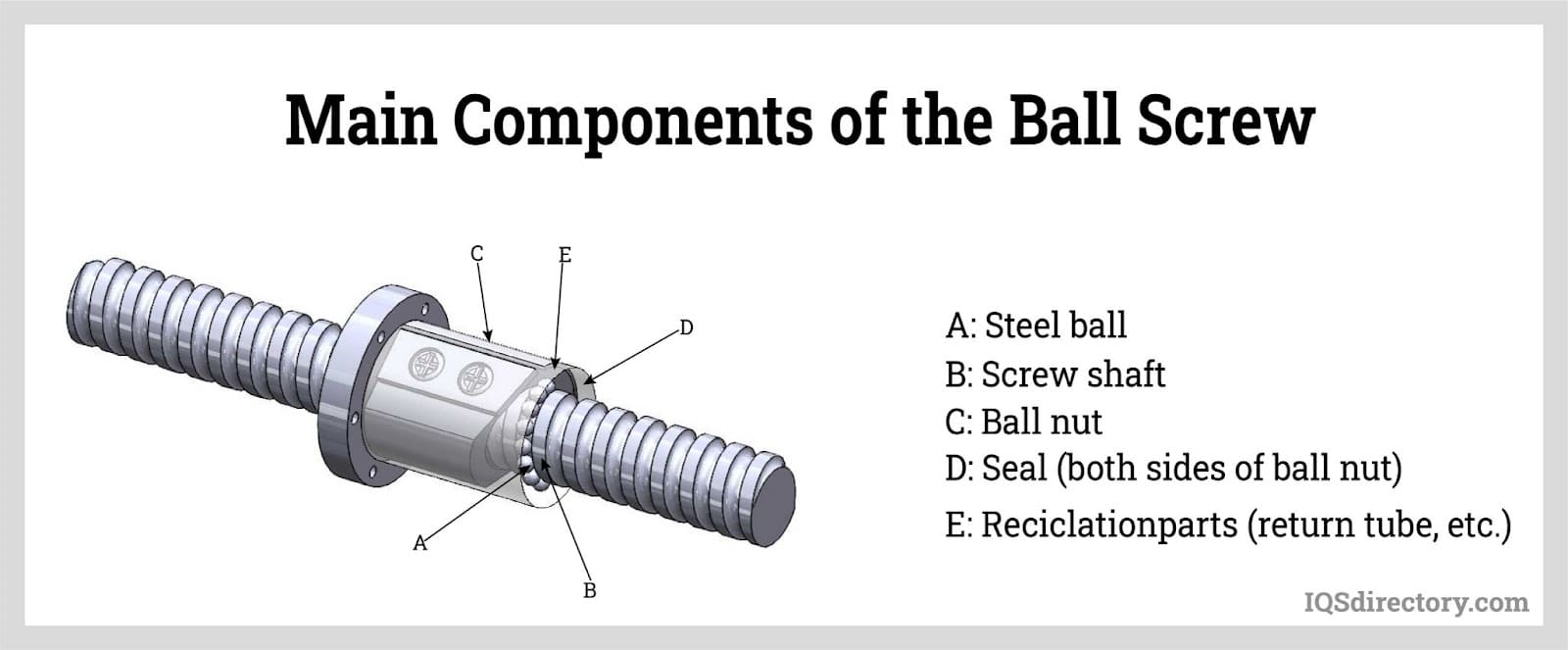

 Ball Bearings
Ball Bearings Ball Screws
Ball Screws Electric Motors
Electric Motors Friction Materials
Friction Materials Gears
Gears Quick Release Couplings
Quick Release Couplings Shaft Couplings
Shaft Couplings Speed Reducers
Speed Reducers Timing Belting
Timing Belting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services